Osteochondrosis -degenerative-dystrophic damage to the intervertebral discs, adjacent joint surfaces and vertebral bodies, spinal tissues characterized by damage to the spinal apparatus.
Often, pathological processes in osteochondrosis primarily affect the bones and ligaments. We learn that the disease has already begun, usually in the presence of complications - pain, emotional disorders, muscle atrophy, disorders of internal organs.
Who suffers from osteochondrosis?
Currently, 40-90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis. The disease most often affects people over 30 years. However, the first symptoms of osteochondrosis may appear during adolescence.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis of the spine
- The first stage in the development of osteochondrosis.
Dehydration of the nuclear pulp begins. This reduces the height of the disk. Cracks appear in the annulus fibrosus, but the pathological process does not extend beyond the intervertebral disc.
- The second stage in the development of osteochondrosis.
As a result of a decrease in the height of the disc, the points of attachment of the muscles and ligaments of the two adjacent vertebrae converge. Therefore, muscles and ligaments shake. This can lead to excessive mobility of the two vertebrae relative to each other, ie. instability of the vertebral-motor segment occurs. This stage is characterized by the formation of spondylolisthesis, the sliding or displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other.
- The third stage in the development of osteochondrosis.
During this period, the most obvious morphological changes of interest to the intervertebral discs occur in the first place: prolapse and protrusions of the discs occur. The articular apparatus of the vertebral-motor segment also suffers. Subluxations occur in the intervertebral joints and invertebrate joints, arthrosis occurs.
- The fourth stage in the development of osteochondrosis.
At this stage, adaptive changes occur in the affected parts of the lower back. The body tries to overcome the excessive mobility of the vertebrae and immobilize the spine to maintain its support and protective functions. In this regard, marginal bone growths occur on the adjacent surfaces of vertebral bodies, in other words, in osteophytes. An osteophyte growing in the "wrong place" causes microtrauma of the nerve root. In the fourth stage, fibrous ankylosis processes usually begin in the intervertebral discs and joints. As a result, the vertebral motor segment is covered with a crust - the clinical manifestations are reduced.
Causes of osteochondrosis
In each of the many existing theories about the development of osteochondrosis, various causes responsible for the onset of the disease, such as mechanical injury, hereditary predisposition, or metabolic diseases, are accepted. A particular difficulty in determining the cause of osteochondrosis is the fact that the disease can occur in both physically fit and less trained adults and young people. There is a widespread belief that the cause of osteochondrosis is the deposition of spinal salts: the alleged X-ray salt can be seen in the form of "growth" or "hook" in the spine. For many patients, the only cause of this condition is the well-known "salt deposition" when there is a tingling and tingling in the joints during movement, as if sand had been poured between them. Such misconceptions are not generally harmless: a correct idea of how to treat a disease can be identified based on an analysis of the underlying causes.
The term "osteochondrosis" comes from the Greek roots osteon - "bone" and chondr - "cartilage". The end of "-Oz" means that bone and cartilage disease is not associated with inflammatory processes, is degenerative-dystrophic, ie the basis of the disease is malnutrition of tissues and, consequently, degeneration. its structure. Like all living tissues, the bone tissue of the vertebrae and the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs are constantly rebuilding and renewing themselves. Under the influence of regular physical force, it gains strength and elasticity, and in the absence of load, the strength of tissues decreases.
This is due to the characteristics of nutrition and blood supply to bone and cartilage tissues. Adult discs do not have their own veins; receives nutrients and oxygen from neighboring tissues. Therefore, for proper nutrition of the discs, it is necessary to activate the blood circulation in the tissues surrounding the discs. And this can only be achieved with intense muscle work.
According to its composition, the intervertebral disc can be divided into two parts: the gelatin nucleus, which has a strong fibrous ring in the center and around it, which gives the disc elasticity. Due to the deterioration of the nutrition of the intervertebral discs, the complex structure of biopolymer compounds that make up the pulposus nucleus is destroyed. The gelatinous core reduces moisture content and becomes more brittle. When subjected to small overloads, the gelatinous nucleus may disintegrate. This further reduces the elasticity. There is also a decrease in the strength of fibrous disc rings. All these factors create the basis and lead to the development of osteochondrosis.
To restore the function of the spine, it is necessary to mobilize the scarring, compensatory abilities of the spine and the musculoskeletal system as a whole in the damage of the intervertebral disc, to remove the "thorns" in the vertebrae, not the resorption of "salt deposits". An X-ray after treatment may show that the shape of the spine has not changed. And the famous "thorns" are not the cause of osteochondrosis, but the result of adaptation processes. Marginal growths increase the area of the supporting surface of the vertebral body. By increasing the area, the specific pressure decreases, which allows to compensate for the decrease in the strength and elasticity of the intervertebral disc.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine are accompanied by calcification (calcification) of damaged discs, separate parts of the joint ligaments, cartilage, capsules. This process can only be called a salt precipitate. Thus, this is not the cause of osteochondrosis, but only a consequence and final stage of the above process.
The reverse development of structural changes in the spine is almost impossible. But minimizing them is a very real problem. If no effort is made to keep the spine in the condition achieved by treatment, the pain may recur.
Clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis
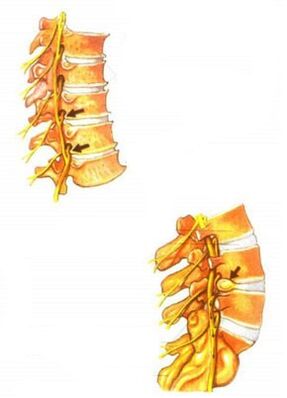
The clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are very diverse. They depend on the stage of development of osteochondrosis. The main clinical symptoms of osteochondrosis occur when the pathological process extends to the posterior part of the annular fibrosis and the posterior longitudinal tortoise. Depending on the stage of degeneration of the intervertebral discs, irritation, compression or impaired transmission of spinal cord roots, vasoconstriction or compression of the spinal cord occurs. Various neurological syndromes develop - reflex and compression.
The main cause of pain in osteochondrosis is the so-called nerve root irritation. In this case, circulatory disorders occur, edema occurs, and in the future may develop fibrosis of the surrounding structures, which is accompanied by an increase in sensitivity of the roots to various influences (movements in the affected part of the spine, etc. )).
Vascular disorders in osteochondrosis are often associated with impaired vasomotor innervation. Mechanical compression of blood vessels by osteophytes is also possible, for example, in the cervical spine.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
One of the features of spinal osteochondrosis that aggravates the process is its very broad symptomatology. The disease can manifest itself in completely different parts of the body. There may be pain or numbness in the extremities or discomfort and pain in the internal organs. At the same time, often a person in no way associates pain in the heart, abnormalities in the functioning of the genitals, headaches, osteochondrosis, and pain and numbness in the legs and spine in general. "Treatment" of the symptoms of osteochondrosis directly with the help of various types of painkillers, all kinds of advertised drugs, dietary supplements and other methods. However, this road situation worsens. Osteochondrosis continues to develop, and the treatments used do not lead to significant improvement, except to temporarily relieve the pain at best, and can do more harm to the body at worst.
Thus, it is important to carefully analyze your situation and the changes that take place in it. It is necessary to start moving in the right direction: consult a doctor in a timely manner, undergo the necessary diagnosis, and only after the correct diagnosis, start treatment under the supervision of the attending physician.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis include, first of all, back pain and discomfort. At the same time, pain can be periodic, unstable, appearing now and then disappearing. But the first feeling of discomfort or pain in the spine should make you think. The appearance of the first pain is at least a signal to pay attention to it, try to remember the cause. This is due to the lifting of a heavy object, sudden movement, falling, etc.
Another symptom of osteochondrosis is discomfort or back pain (arm or leg) accompanied by pain and numbness in the extremities. The pain most often spreads to the left limb, ie the left arm or leg. In addition, the pain manifests itself not only in the heart, but also in the back and spine, for example, in the ribs and so on. In this case, it is especially important to pay attention to the nature of the pain change, depending on the patient's movements, and to compare the sensations of back pain, for example, with pain in the legs. If the patient sits for a long time and there is pain or numbness in the leg, discomfort in the lower back, and the pain disappears after a little warming up or walking, then this will be an indirect sign. lumbar osteochondrosis. The same picture can be with the neck and arms. In summary, the main symptoms of osteochondrosis are back pain and discomfort. If these symptoms coincide with pain in other parts of the body, osteochondrosis can be complicated by a bulge, a herniated disc, and a pinched nerve.
In addition, I would like to emphasize that even with the onset of the first pain in the spine, it is necessary to pay special attention to this concern. After all, osteochondrosis can be weak or not manifest for a long time. At the same time, an increasing number of discs will continue to develop successfully in the spine, causing degradation. Therefore, timely consultation with a doctor will allow you to diagnose osteochondrosis at an earlier stage, which will facilitate treatment.
Osteochondrosis and salt deposition
Osteophytes, or hook-like growths of the spine, occur to reduce the load on the intervertebral discs. In this case, the appearance of osteophytes impairs the mobility of the intervertebral joints.
It is a common misconception that salt deposition in daily life is a major cause of osteochondrosis. Therefore, the treatment of osteochondrosis using a salt-free diet is meaningless.
The most common complaints of the spine
The most common complaints in osteochondrosis are:
- Discomfort in different parts of the spine. The pain can vary from small, dull, strong, sometimes very strong and unbearable - with lumbago.
- Here is the increasing fatigue, both physically and mentally.
- Sensory disturbances in the legs and various parts of the body, coldness of the arms or legs.
- Pain spreading to the legs along the nerve trunks.
- Pain in the scapula, spread to the shoulder, as well as pain in the neck and back of the head.
- A frequent companion of cervical osteochondrosis is headache, dizziness. Increased visual fatigue or decreased visual acuity are often observed.
- With the defeat of the lumbar-sacral region, disorders of the reproductive system often occur - various sexual disorders. Therefore, most men have an increase in sexual potency after treatment. In women, the normal functioning of the lumbosacral zone increases the likelihood of conception and promotes a comfortable pregnancy.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
To diagnose osteochondrosis, it is necessary to collect a medical history. In this case, it is very important to identify the patient's complaints. Certain symptoms of osteochondrosis are quite typical. Others should be different from the symptoms of other diseases. It is important to be able to simulate various diseases of the nervous, vascular, trophic diseases that occur in osteochondrosis, such as angina pectoris, gastritis, gastric ulcer, acute surgical diseases of the abdominal organs. Therefore, each symptom must be thoroughly analyzed to avoid misdiagnosis and subsequent misdiagnosis.
When collecting medical history, including patient complaints, current medical history, and patient life, the physician pays attention to age because osteochondrosis is more common in older people and the evolution of symptoms from the time they appear until the patient leaves. to the doctor. Osteochondrosis is characterized by slow development, with periods of exacerbation periodically replaced by periods of remission. Additional research methods are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
X-ray examinations for osteochondrosis
The most accessible and well-informed method for the diagnosis of osteochondrosis is X-ray examination. There are several types of X-rays for the diagnosis of this disease:
Flat radiography of the spine is the simplest X-ray method for the diagnosis of osteochondrosis. Its essence is to obtain radiographs of whole or individual segments of the spine. Visual radiography is often performed - the location of the spinal lesion is determined based on the symptoms of the disease and the patient's complaints. X-rays of the spinal segment affected by osteochondrosis show a decrease in the thickness of the intervertebral discs (atrophy), which manifests itself as a decrease in the space between the vertebrae, the appearance of bone. enlargement of vertebral bodies - osteophytes, partial solution - resorption of bone tissue of the vertebral body, changes in the shape of the spinal segment, for example, smoothing of the lord lordosis.
Myelography is a more complex and dangerous diagnostic method. During such an examination, a certain amount of contrast fluid is injected into the spinal canal. The risk of this test is the possibility of an allergic reaction to a contrast agent or spinal cord injury during perforation of the spinal canal. Thanks to myelography, it is possible to determine the internal structure of the spinal canal. This method is especially well-known for the diagnosis of spinal hernias.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most modern, but also the most expensive and difficult to diagnose osteochondrosis. These diagnostic methods are generally used when it is necessary to differentiate between osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spine with similar symptoms, for example, tumors of the spinal canal.
It is mandatory to conduct a neurological examination of a patient with osteochondrosis in order to thoroughly assess the patient's condition. Thanks to a neurological consultation, it is possible to determine the location and extent of motor and sensory disorders.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
The clinic provides effective treatment for all forms of osteochondrosis. The treatment is outpatient. Treatment is based on a comprehensive program aimed at quickly eliminating the underlying syndrome and the cause of the pain. The following methods can be used as part of complex therapy:
- acupuncture;
- vacuum therapy;
- gentle manual therapy (post-isometric relaxation);
- laser therapy;
- pharmacopuncture;
- dry towing;
- magnetopoint;
- electrical stimulation and other treatments.
The average course of treatment is 10-15 sessions, and the elimination of acute pain syndrome is between 1 and 3 sessions.
The sooner treatment is started, the better the result!
Is it possible to completely eliminate osteochondrosis?
It depends on the form of the disease, the severity, accuracy and timeliness of treatment. Complete treatment is possible only in the initial stages.
However, it is possible to prevent the exacerbation of osteochondrosis and not feel pain for years. If a person has osteochondrosis, but does not feel uncomfortable now, it does not mean that it has passed without a trace. There may be changes in the spine.
The main task is to stop the development of the disease and do everything possible to eliminate some pathological changes in the spine, to eliminate or reduce symptoms (back pain, colds and headaches of the arms, legs, head, etc. ).



































