Severe knee pain indicates a problem in the joint. The peculiarity of the knee joint is that it carries the main load during movement and physical force, and therefore is often damaged. It is difficult to straighten the affected knee, so it is very important to take measures to eliminate the cause of pain in a timely manner.
The main reasons
Causes of knee pain can be:
- Injuries (acute injuries).They are the most common reason. They occur after a strong blow, excessive bending of the joint and a sharp fall on it. With mechanical injury, there is severe pain, swelling, tingling, numbness, discoloration of the skin in the joint area.
- Osteoarthritisis the destruction of joint tissues. Gonarthrosis is primary and secondary. The primary disease affects the elderly, and the secondary causes the consequences of injuries or aggravation of other diseases (eg, rheumatoid arthritis). Symptoms: pain and stiffness in the joint. With a long course of gonarthrosis, joint action may be impossible.
- Arthritis- inflammatory disease. Different symptoms: increased pain with movement, increase in joint size, fever in the affected knee, sometimes redness.
- Meniscopathy- Damage to the meniscus, manifested by severe pain. In the absence of appropriate treatment, the transition to a chronic form is possible, resulting in the development of osteoarthritis.
- Vascular diseases. Thrombosis or embolism (blockage) of the arteries that supply the knee joint makes it impossible to walk, leading to osteonecrosis of the articular cartilage. There is no effective treatment for osteonecrosis. Arthroplasty of the affected joint is performed.
- periarthritis- It is an inflammation of the articular sac and surrounding tissues. With periarthritis, there is pain without a clear localization in the area of the knee joint. Periarthritis is the most common post-traumatic complication.
- BursitisInflammation of the synovial sac (bursa). Bursitis can be caused by overuse of the joint, infection or injury. The disease is characterized by severe persistent pain, but freedom of movement is preserved.
- TendinitisIt is an inflammation of the ligaments and tendons. Symptoms include swelling and pain in the affected area. They increase with flexion-extension of the knees. Prolonged symptoms of tendinitis are an indication of tendinosis.
- Baker's cyst- This is a complication of trauma, gonarthrosis or hemarthrosis. Baker's cyst is an accumulation of joint fluid in the popliteal sac. Pathological knee is characterized by pain during bending and discomfort during movement. It is highly recommended not to squat to prevent complications.
- Osteomyelitis of the bones of the footHematogenous osteomyelitis is a purulent disease associated with an infection that results from an open fracture or postoperative complication. The most common infectious agent is staphylococci.
Types of pain
There are the following types of knee pain:
- While squatting. It is usually caused by joint diseases, viral infections, lack of physical activity, improper diet. observed in athletes. If your knees hurt during squats, then the exercises should be stopped. You should consult a doctor for long and frequent pain.
- While bending the legs. This is one of the most common joint problems. Osgood-Schlatter disease, damage to ligaments and meniscus, Baker's cyst, infectious lesions, etc. observed with. When pain occurs, it is necessary to limit the load on the foot, refrain from playing sports, wear comfortable orthopedic shoes.
- After the run. Osteoarthritis, bursitis, synovitis, etc. associated with diseases such as. In this case, the normal functioning of the joint stops and begins to collapse under heavy loads. These diseases require timely treatment, otherwise complete loss of motor function is possible.
- Crunch. If there is no swelling, pain and stiffness in the movement, there is nothing to fear. However, this symptom can be caused by a dangerous disease - articular cartilage is damaged and severe pain appears. It is very important to start treatment of this disease on time.
Diagnostics
You can diagnose the cause of pain in the following ways:
- General blood test. Anemia, leukocytosis, etc. allows you to detect.
- Blood chemistry. Detects an increase in uric acid in gout.
- X-ray examination. This method allows you to detect pathology of bone tissue. With its help, fractures, osteomyelitis and osteoarthritis are diagnosed. X-ray examinations are complemented by computed tomography (CT). Menisci, ligaments, bursae, and other soft tissues are not visible on X-rays and CT scans.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging). This is modern research. With its help, joint pathology of the soft tissues (menisci, ligaments, etc. ) is diagnosed.
- Bone puncture biopsy. It is performed when osteomyelitis or bone tuberculosis is suspected.
- Arthroscopy. It is used for both diagnosis and treatment, for example, with damage to the meniscus.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination). These include suspected traumatic injuries, osteoarthritis, meniscus disease, and more. is a screening study conducted in cases. Ultrasound results should be confirmed by radiography (CT) and / or MRI.
Treatment
Treatment should be comprehensive and include both conservative methods and surgery. Let's look at them in more detail:
conservative methods
In case of exacerbation, treatment should eliminate pain and swelling, and then restore normal joint mobility. It is not recommended to move without assistance for the first time after an injury.
The basis of treatment is anti-inflammatory therapy. This involves the use of the following agents: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pyrazolone derivatives, indoleacetic acid derivatives, oxycamines, glucocorticoids.
The following procedures are prescribed to strengthen the immune system: cryopheresis, plasmapheresis, hemosorption, plasma filtration, immunostimulants.
The specific drug and method of treatment is selected by the attending physician.
Conservative treatment also includes ice compresses or hot compresses to improve blood microcirculation in the affected area to relieve pain.
With hemarthrosis, the joint is punctured and the blood collected as a result of the trauma is removed.
Conservative treatment also includes physiotherapy: massage, therapeutic exercises and spa rehabilitation. If necessary, the doctor prescribes a special diet that provides limited calorie content.
Chondroprotectors are used to nourish cartilage and reduce destructive processes.
The most common physiotherapy methods are magnetotherapy, laser therapy, cryotherapy, acupuncture.
Special shoes and knee pads - orthoses are used with gonarthrosis. These shoes help to normalize gait, and knee pads correct the diseased joint.
Surgical intervention
If the required joint stability cannot be achieved after conservative treatment, surgery is indicated.
The most common surgical methods are arthroscopy and arthroplasty.
Arthroscopy is a method that relieves joint pain and increases mobility. This method of treatment not only eliminates the underlying disease, but also allows the introduction of drugs into the joint space that reduce inflammation.
Doctor's advice
A clear therapeutic effect in stage 2 and even stage 3 osteoarthritis is given by hyaluronic acid drugs administered intraarticularly. The use of hyaluronic acid is considered an alternative to arthroplasty when it is not possible due to therapeutic contraindications. This is medical manipulation, there are contraindications.
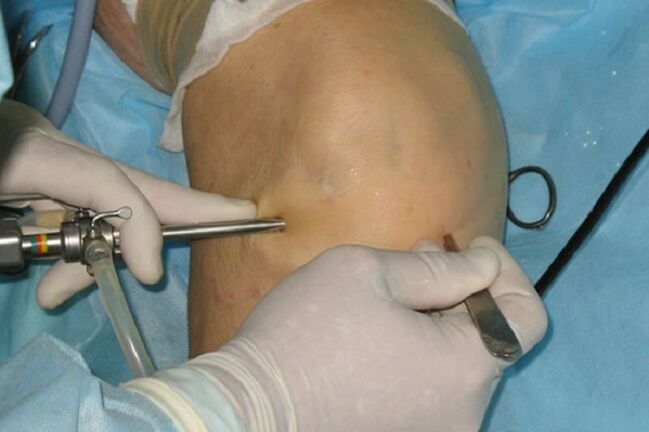
The technique is implemented with the following problems:
- damage to the meniscus and cartilage;
- ligament hernia;
- presence of joint foreign bodies;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- intraarticular fractures.
During postoperative rehabilitation, it is recommended to strictly follow medical recommendations by performing therapeutic exercises, avoiding unreasonably early loading on the limb.
Endoprosthesis (arthroplasty) is the operation of replacing damaged parts of the knee joint with an artificial implant (endoprosthesis).
More than 95% of endoprostheses covered by compulsory health insurance have a lifespan of 10-15 years and must be replaced. Today, far from all regions, endoprosthesis replacement, unlike the initial operation, can be provided with compulsory health insurance. After 10-15 years, not all patients are able to have a second operation due to cardiovascular and other somatic risks. Therefore, it is not worth rushing with endoprosthetics. I recommend this operation only when all other treatment options are exhausted.
When it is not possible to restore the painless function of the knee joint by conservative methods and arthroscopy, endoprostheses are performed. Purulent complications are possible after arthroplasty. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent them. After endoprosthetics, the patient requires long-term rehabilitation (up to 6 months).
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can be useful in relieving pain, but they should be carried out in parallel with traditional treatments.
Be sure to consult a doctor when using folk remedies.
Here are some popular methods:
- Ointment. Prepare 1 tablespoon for knee pain. l. hypericum and 2 tbsp. l. yarrow, crush them. Melt 1 tablespoon in a water bath. l. Vaseline. The grass is poured into hot Vaseline and rubbed into a homogeneous mass. This ointment should be applied to sore knees at night.
- A mixture based on rye seeds. You need to take 250 g of rye seeds, pour them with 2 liters of water and bring to a boil. After cooling, the mixture is filtered and 500 g of vodka, 1 kg of honey, 3 tsp are added. barberry root. The mixture is thoroughly mixed and left for 21 days in a dark place. It is recommended to use a mixture of 3 tbsp. l. before meals. It is required to drink 9 liters of the mixture during treatment.
If you have knee pain, do not panic. However, if the pain persists for a long time, you must see a doctor. This will avoid many problems.



































